147059-75-4
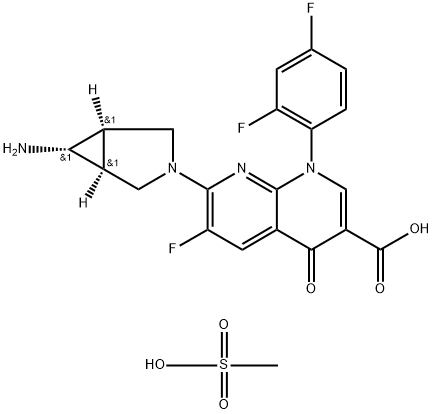 147059-75-4 結(jié)構(gòu)式
147059-75-4 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
曲伐沙星甲磺酸鹽
CP 99219-27
Unii-0p1lko80wn
Trovafloxacin MonoMeth
Trovafloxacin Methanesulfonate
Trovafloxacin monomethanesulfonate
Trovafloxacin mesylate - CP 99219 mesylate
7-[(1S,5R)-6-amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex-3-yl]-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid
7-[(1α,5α,6α)-6-Amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex-3-yl]-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylicacidmesylate
(1α,5α,6α)-7-(6-Amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex-3-yl)-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid methanesulfonate
安全數(shù)據(jù)
常見問題列表
IC50: 4 μM (Pannexin 1 channel (PANX1))
Gram-positive, Gram-negative and anaerobic organisms
DNA gyrase
Topoisomerase IV
Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; HepG2 cells) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF; 4 ng/mL) incubation induces apoptosis and increases leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in HepG2 cells.
Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; HepG2 cells) and TNF (4 ng/mL) incubation increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα.
Trovafloxacin prolongs TNF-induced activation of MAPKs and IKKα/β activation in HepG2.
Trovafloxacin is a potent inhibitor of TO-PRO-3 uptake by apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin also inhibits ATP release from apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin does not inhibit caspase 3/7 activation, or caspase-mediated PANX1 cleavage during apoptosis.
Trovafloxacin is equally active against both penicillin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococci, with MICs of 0.06-0.25 mg/mL reported for more than 700 isolates. The MICs of Trovafloxacin at which 90% of isolates are inhibited for 55 isolates of pneumococci is 0.125 μg/mL.
Apoptosis Analysis
| Cell Line: | HepG2 cells |
| Concentration: | 20 μM |
| Incubation Time: | 24 hours |
| Result: | Showed a gradual increase of Annexin V-staining and an increased leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) at 24 h. |
RT-PCR
| Cell Line: | HepG2 cells |
| Concentration: | 20 μM |
| Incubation Time: | 24 hours |
| Result: | Caused a higher increase in the transcription of A20 and IκBα in HepG2 cells. |
Trovafloxacin (150 mg/kg; oral administration; male C57BL/6 J mice) treatment disrupts TNF-induced p65 nuclear translocation. Trovafloxacin treatment increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα.
Trovafloxacin, when administered in combination with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or TNF to mice induces severe liver toxicity associated with vast apoptotic areas in the liver, increased serum levels of alanine amino transferases (ALT) and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
| Animal Model: | Male C57BL/6 J mice (9-11-week-old) injected with recombinant murine TNF ion |
| Dosage: | 150 mg/kg |
| Administration: | Oral administration; once |
| Result: | Showed a greater number of cells with increased nuclear/cytoplasmic p65 ratio in liver. |

