131334-43-5
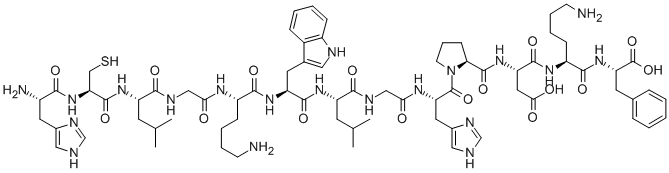 131334-43-5 結(jié)構(gòu)式
131334-43-5 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
髓鞘蛋白脂蛋白H-HIS-CYS-LEU-GLY-LYS-TRP-LEU-GLY-HIS-PRO-ASP-LYS-PHE-OH
PLP (HUMAN, BOVINE, DOG, MOUSE, RAT)
Myelin Proteolipid Protein (139-151) (1)
6:PN:WO2012154215 SEQID:5 unclaimed protein
HIS-CYS-LEU-GLY-LYS-TRP-LEU-GLY-HIS-PRO-ASP-LYS-PHE
H-HIS-CYS-LEU-GLY-LYS-TRP-LEU-GLY-HIS-PRO-ASP-LYS-PHE-OH
PLP (139-151) (DEPALMITOYLATED) (HUMAN, BOVINE, DOG, MOUSE, RAT)
MYELIN PROTEOLIPID PROTEIN (139-151) (HUMAN, BOVINE, DOG, MOUSE, RAT)
LIPOPHILIN (139-151) (DEPALMITOYLATED) (HUMAN, BOVINE, DOG, MOUSE, RAT)
MYELIN PROTEOLIPID PROTEIN (139-151) (DEPALMITOYLATED) (HUMAN, BOVINE, DOG, MOUSE, RAT)
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
常見問題列表
Severe clinical and histological EAE could be induced by adoptive transfer of the peptide-specific T cell line and 3 of 4 T cell clones. The T cell line/clones all responded strongly to PLP (139-151) in in vitro proliferative assays. Line SPL and all of the clones show strong proliferative response to the whole PLP molecule and to PLP (139-151).
PLP (139-151) induces acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in SJL/J mice. Beginning on Day 9, the mice treated with PLP (139-151) show signs of EAE and the disease progressed rapidly to paralysis. Central nervous system inflammation, edema, gliosis, and demyelination are found in all mice killed between Days 10 and 28. Young male SJL mice immunized with a major encephalitogenic peptide of myelin, PLP 139-151, develop initial clinical and histological symptoms of EAE with a severity similar to age-matched females; however, unlike females, male mice does not relapse. Significant T cell proliferation to PLP 139-151, but not to other PLP and myelin basic protein (MBP) epitopes, is observed in both males and females during the initial episode, recovery, and first relapse of clinical disease.
