1256493-34-1
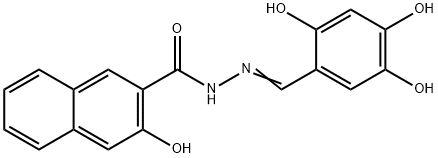 1256493-34-1 結(jié)構(gòu)式
1256493-34-1 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
DYNGO?4A,新型的動(dòng)力抑制劑
HYDROXY DYNASORE游離
3-羥基-N′-((2,4,5-三羥基苯基)亞甲基)-2-萘酰肼
Dyng
Dyngo-49
Dyngo-4a
Hydroxy-Dynasore
3-Hydroxy-N′-[(2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]naphthalene-2-carbohydrazide
3-Hydroxy-2-naphthalenecarboxylic acid 2-[(2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)methylene]hydrazide
3-Hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid 2-[(2,4,5)-trihydroxyphenyl)methylene]hydrazide
2-Naphthalenecarboxylic acid, 3-hydroxy-, 2-[(2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)Methylene]hydrazide
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
安全數(shù)據(jù)
常見問題列表
Dynamin is a large GTPase enzyme that severs membrane‐bound clathrin‐coated vesicles. Endocytosis internalizes portions of cells’ plasma membrane along with extracellular material, is fundamentally important in cell physiology. Hydroxy Dynasore inhibits Dynamin I (Dyn I) activity with IC 50 values of 2.7 μM and 0.38 μM with or without 0.06% Tween‐80 in the GTPase assay. Hydroxy Dynasore shows an IC 50 of 5.7 μM in clathrin‐mediated endocytosis (CME) assay for inhibition of Tfn‐A594 uptake in U2OS cells. Hydroxy Dynasore shows IC 50 values of 0.38 μM and 1.1?μM in absence of Tween-80, and exhibits IC 50 values of 4.9 μM and 30.0?μM in presence of Tween-80, respectively. Hydroxy Dynasore is 2.1‐fold selective for DynI versus DynII from Sf21 cells] and DynII (recombinant protein from Sf21 cells) in this GTPase assay. Hydroxy Dynasore prevents the uptake of BoNT/A-Hc in cultured hippocampal neurons and in motor nerve terminals. Hydroxy Dynasore (1-100μM; 20 min prior to the addition of Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc) results in depolarization of Hippocampal neurons, it dose-dependently inhibits internalization of Alexa Fluor 488-BoNT/A-Hc with an IC 50 of 16.0 ± 1.2 μM.
Hydroxy Dynasore (intraperitoneal injection; 30 mg/kg; 1.5-2 h before BoNT/A injection) provides protection again BoNT/A-induced paralysis in the phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm twitch model in CD-1 mice.
| Animal Model: | CD-1 mice. |
| Dosage: | 30 mg/kg |
| Administration: | Intraperitoneal injection; 1.5–2 h before BoNT/A injection |
| Result: | Protected BoNT/A-induced paralysis in vivo. |


