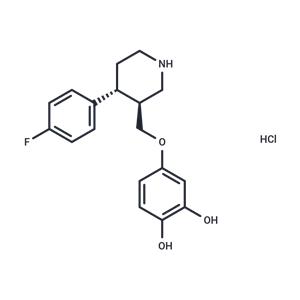
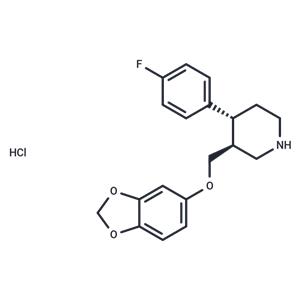
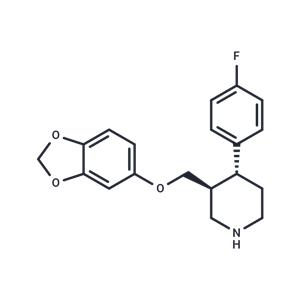
Desmethylene Paroxetine hydrochloride NEW
| Price | $155 | $288 | $825 |
| Package | 5mg | 10mg | 50mg |
| Min. Order: | |
| Supply Ability: | 10g |
| Update Time: | 2024-10-28 |
Product Details
| Product Name: Desmethylene Paroxetine hydrochloride | CAS No.: 1394861-12-1 |
| Supply Ability: 10g | Release date: 2024/10/28 |
Product Introduction
Bioactivity
| 名稱 | Desmethylene Paroxetine hydrochloride |
Company Profile Introduction
Target Molecule Corp. (TargetMol) is a global high-tech enterprise, headquartered in Boston, MA, specializing in chemical and biological research product and service to meet the research needs of global customers.
TargetMol has evolved into one of the biggest global compound library and small molecule suppliers and a customer based on 40+ countries. TargetMol offers over 80 types of compound libraries and a wide range of high-quality research chemicals including inhibitors, activator, natural compounds, peptides, inhibitory antibodies, and novel life-science kits, for laboratory and scientific use. Besides, virtual screening service is also available for customers who would like to conduct the computer-aided drug discovery.
You may like
Recommended supplier
| Product name | Price | Suppliers | Update time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $30.00/1kg |
VIP1Y
|
hebei hongtan Biotechnology Co., Ltd
|
2024-03-22 | |
| $10.00/1kg |
VIP1Y
|
Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd
|
2024-06-03 | |
| $0.00/25Kg/Bag |
VIP4Y
|
Sinoway Industrial co., ltd.
|
2022-08-10 |
- Since: 2011-01-07
- Address: 36?Washington?Street, Wellesley?Hills
INQUIRY


 United States
United States