| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Pterostilbene | [CAS]
537-42-8 | [Synonyms]
PTEROSTILBENE
-aminostilbene
PTEROSTILBENE(FG)
PTEROSTILBENE(DS)
Pterostilbene COA
5-Trimethoxy-3'
Pterostilbene 99.8%
5-Trimethoxy-3&rsquo
trans- Pterostilbene
Pterostilbene powder
Soluble Pterostilbene
PTEROCARPUS MARSUPIUM
Pterostilbene Factory
Pterostilbene IN STOCK
BioaActive Pterostilbene
Nanoactive Pterostilbene
| [EINECS(EC#)]
611-041-4 | [Molecular Formula]
C16H16O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00238710 | [MOL File]
537-42-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
256.3 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
89-92 ºC | [Boiling point ]
420.4±35.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.169±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C | [solubility ]
DMSO: >20mg/mL | [form ]
solid | [pka]
9.96±0.26(Predicted) | [color ]
White or off-white | [Odor]
Characteristic | [λmax]
321nm(MeOH)(lit.) | [Stability:]
Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 1 week. | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C16H16O3/c1-18-15-9-13(10-16(11-15)19-2)4-3-12-5-7-14(17)8-6-12/h3-11,17H,1-2H3/b4-3+ | [InChIKey]
VLEUZFDZJKSGMX-ONEGZZNKSA-N | [SMILES]
C1(O)=CC=C(/C=C/C2=CC(OC)=CC(OC)=C2)C=C1 | [LogP]
4.056 (est) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Pterostilbene (PTS, 537-42-8) is a fragrant-smelling hydrocarbon called "styrene", which is a derivative of resveratrol. It is found in blueberries and Pterocarpus marsupium (PM) heartwood. Similar to resveratrol, PTS has anti-inflammatory, anti-thrombotic, anti-cancer, anti-cancer, anti-hyperlipidemia and antibacterial effects.
| [Chemical Properties]
Pterostilbene is a white crystalline powder, sensitive to air, soluble in hot methanol, DMSO, insoluble in water. It is a stilbenoid chemically similar to resveratrol and from the leguminous plant Pterocarpus indicus. | [Occurrence]
Pterostilbene is found in almonds,various Vaccinium berries (including blueberries), grape leaves and vines,and Pterocarpus marsupium heartwood. | [Uses]
Substantial studies demonstrate that pterostilbene has diverse pharmacological activities for the prevention and treatment of diseases including inflammation, cancer, diabetes, and dyslipidemia.
Pterostilbene has been used:
to investigate its anti-oxidative stress activities and the involvement of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2)-antioxidant response element (ARE) signaling pathway
to determine its effects on transcriptional activation of estrogen receptor-α (ERα) in hormone resistant breast cancer cells) | [Definition]
ChEBI: Pterostilbene is a stilbenol that consists of trans-stilbene bearing a hydroxy group at position 4 as well as two methoxy substituents at positions 3' and 5'. It has a role as an antioxidant, an antineoplastic agent, a neurotransmitter, a plant metabolite, an apoptosis inducer, a neuroprotective agent, an anti-inflammatory agent, a radical scavenger and a hypoglycemic agent. It is a stilbenol, a member of methoxybenzenes and a diether. It derives from a hydride of a trans-stilbene. | [Preparation]
Pterostilbene was synthesized from 3,5-dimethoxybenzyl bromide and p-nitrobenzaldehyde by Witting-Hornor reaction, reduction, diazotization and hydrolysis, with a total yield of 53.9%.
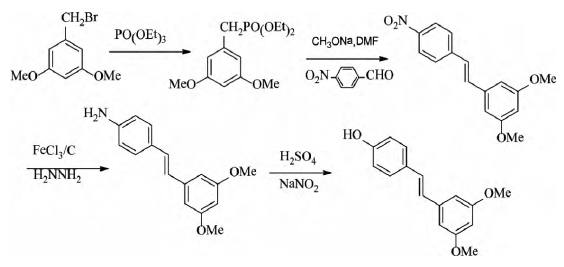 | [benefits]
Pterostilbene(537-42-8) is a naturally-derived stilbenoid structurally related to resveratrol, with potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, pro-apoptotic, antineoplastic and cytoprotective activities. Pterostilbene is known to have many pharmacological benefits for the prevention and treatment of a wide variety of diseases, including ( cancer (McCormack and McFadden 2012), dyslipidaemia (Rimando et al. 2005), diabetes (Amarnath Satheesh and Pari 2006), cardiovascular degeneration (Amarnath Satheesh and Pari 2008) and pain (Hougee et al. 2005).
| [Biological Activity]
A cell-permeable methoxylated analog of Resveratrol that displays antioxidant, anti-proliferative, and hypoglycemic properties. Appears to be a better free radical scavenger than Trolox. Moderately inhibits COX-1 & COX-2 activities (IC50 = 19.8 μM & 83.9 μM, respectively) and induces apoptosis in HL60 cells (IC50 = 70 μM). Also prevents DMBA-induced pre-neoplastic lesions (ED50 = 4.8 μM). Reported to decrease plasma glucose levels in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats comparable to that of Metformin. | [Side effects]
The side effects of pterostilbene are relatively minor, but you still need to pay attention to the dosage. Low-dose pterostilbene supplementation improves cholesterol metabolism and reduces triglyceride levels. Side effects include mild weight loss and muscle pain, but dose adjustment is usually not necessary. | [References]
[1] ESTRELAJOSé M. Pterostilbene: Biomedical applications.[J]. Critical reviews in clinical laboratory sciences, 2013. DOI:10.3109/10408363.2013.805182.
[2] HYUNSOOK KIM Wallace Y Kun Ho Seo. Chemistry of Pterostilbene and Its Metabolic Effects[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00070.
[3] MACICKOVATATIANA. In vivo effect of pinosylvin and pterostilbene in the animal model of adjuvant arthritis.[J]. Neuro endocrinology letters, 2010.
[4] WASAMON NUTAKUL. Inhibitory Effects of Resveratrol and Pterostilbene on Human Colon Cancer Cells: A Side-by-Side Comparison[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011. DOI:10.1021/jf202846b. |
|
|