| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
BISPHENOL A DIGLYCIDYL ETHER RESIN | [CAS]
25068-38-6 | [Synonyms]
e828
e1001
e1004
164Sv
solids
Der331
epon820
liquids
CYD-128
erl-2795
epon1001
epon1007
Epon1009
epidian5
UP 5-207
EPIDIAN3
D.E.R.?330
epikote828
epikote1001
epikote1004
epikotedx6002
aralditegy250
DER 332 RESIN
EPON RESIN 828
EPON(R) RESIN 828
epoxyresinerl-2795
araldite 506epoxy resin
Epoxy resin (EPON 1001)
epichlorhydrin-bisphenol
Araldite? 502 epoxy resin
epichlorhydrin-bisphenolaresin
Araldite(R) 502 epoxy resin
BisphenolA,epichlorohydrinpolymer
EPICHLOROHYDRIN/BISPHENOLAPOLYMER
BISPHENOL A DIGLYCIDYL ETHER RESIN
bisphenol A/ epichlorohydrin resin
Bisphenol A-epichlorohydrin copolymer
BisphenolA,(chloromethyl)oxiranepolymer
4,1-phenyleneoxymethylene)]bis[oxirane]
homopolymerofdiglycidyletherofbisphenola
4-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]phenol
bisphenol A/ epichlorohydrin resin, solid
bisphenol-A-(epichlorohydrin) epoxy resin
bisphenol A/ epichlorohydrin resin, liquid
bis(4,1-phenyleneoxymethylene)]bis[oxirane]
2,2-Diphenylolpropane-epichlorohydrin polymer
lowmolecularweightsoliddgebpa-basedepoxyresins
4,4-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOLEPICHLOROHYDRINRESIN
lowmolecularweightliquiddgebpa-basedepoxyresins
4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOL/EPICHLOROHYDRIN COPOLYMER
2,2-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane-epichlorohydrin polymer
2,2-Bis(hydroxyphenyl)propane-epichlorohydrin copolymer
2,2-Bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)propane-epichlorohydrin polymer
2,2-Bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)propane-epichlorohydrin copolymer
2,2-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane-epichlorohydrin copolymer
PHENOL44METHYLETHYLIDENEBISPOLYMERWITHCHLOROMETHYLOXIRANE
2,2-Bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)propane-epichlorohydrin condensate
diglycidyletherofbisphenola-basedepoxyresins,lowmolecularweight
phenol,4,4’-isopropylidenedi-,dimerwith1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane
Poly(Bisphenol A-co-epichlorohydrin) average Mw ~40,000, pellets
2-(chloromethyl)oxirane:4-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]phenol
(Chloromethyl)oxirane,4,4’-(1-methylethylidene)bisphenolcopolymer
4,4’-(1-methylethylidene)bis-phenopolymerwith(chloromethyl)oxirane
4’-(1-methylethylidene)bisphenol,-polymerwith(chloromethyl)oxirane
phenol,4,4’-isopropylidenedi-,monomerwith1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane
phenol,4,4’-isopropylidenedi-,polymerwith1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane
phenol,4,4’-isopropylidenedi-,tetramerwith1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane
Phenol,4,4’-(1-methylethylidene)bis-,polymerwith(chloromethyl)oxirane
4,4'-Isopropylidenebis(phenol)·1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane polycondensate
POLYMEROF4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOLAND1-CHLORO-2,3-EPOXYPROPANE(LIQUID)
4,4’-(1-methylethylidene)bisphenol,-,polymerwith2,2’-[(1-methylethylidene)
4,4’-(1-methylthylidene)bisphenol,polymerwith2,2’-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(
2,2’-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(4,1-phenyleneoxymethylene)]bis[oxirane],homopoly
reaction product: bisphenol-A-(epichlorhydrin) epoxy resin (number average molecular weight ≤ 700)
Reaktionsprodukt aus Bisphenol-A oder -F mit Epichlorhydrin (Molekulargewicht <700, Gehalt an freiem Epichlorhydrin <20 ppm, nicht in R40 oder R45 eingestuft) | [EINECS(EC#)]
500-033-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C18H21ClO3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD03792911 | [MOL File]
25068-38-6.mol | [Molecular Weight]
228.286 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
64-74 °C | [Boiling point ]
114-118 °C | [density ]
1.18 | [Tg]
100 | [vapor pressure ]
0Pa at 19.85℃ | [Fp ]
78 °C | [storage temp. ]
room temp | [solubility ]
Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Soluble), Methanol (Sparingly) | [form ]
pellets | [color ]
Gardner: ≤3 | [Water Solubility ]
7mg/L at 25℃ | [InChIKey]
IISBACLAFKSPIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [LogP]
3 at 25℃ | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Bisphenol A epichlorohydrin polymer (25068-38-6) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Introduction]
Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA) is a pale yellow liquid epoxy compound formed by the polycondensation of epichlorohydrin (ECH) and bisphenol A (BPA). Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA) can be called a small-molecule adhesive. Epoxy groups located at both ends of the molecule can undergo reactions of ring-opening, cross-linking and solidity with amines, anhydrides, and other curing agents of epoxy resins. Therefore, they are effective adhesion for most substrates such as glass, ceramics, silicon wafers, and polymer materials. It is the lowest molecular weight epoxy resins, and also used as the packaging material for coatings, adhesives, insulating paints, semiconductors, and integrated circuits and other electronic components. In recent years, DGEBA has been used for the inner coating of packaging materials such as canned food.
| [Preparation]
Add bisphenol A and epichlorohydrin in the amount of 1:4 into a three-necked flask equipped with a reflux device, place it in a constant-temperature oil bath, melt it with 70 °C of heat, and dropwise 28.57% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution with a dropping funnel, in which the ratio of the amount of sodium hydroxide and bisphenol A is 4:1. When dropping is completed within half an hour, heat it for 12-24 hours under temperature 70-80°C�����。 Stop the heating after bisphenol A is completely disappeared validated by TLC method. Cool the mixture to room temperature; add extractant toluene/water (volume ratio 2:1) and stir it at room temperature for half an hour. Transfer to a pear-shaped separatory funnel to separate the liquid, continue washing and separating with deionized water until the solution turns to neutral from alkaline. Distillation and vacuum distillation are used to remove toluene and unreacted epichlorohydrin, respectively. Use a solvent mixture of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (volume ratio 3:1) a developing solvent to purify it by column chromatography according to the above procedure to obtain DGEBA.
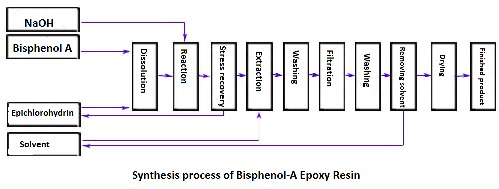
This process, also known as a one-step process, is commonly used for the preparation of low and medium molecular weight bisphenol A epoxy resins.
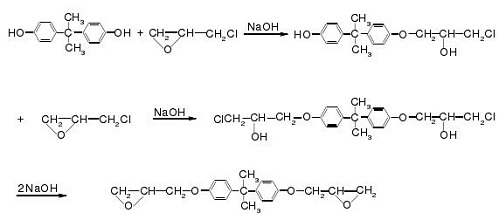
When the low-molecular-weight bisphenol A epoxy resin is continuously reacted with bisphenol A, the obtained bisphenol A epoxy resin has a high polymerization with a relative molecular mass 1400 or more. This is called a two-step method. When the number-average molecular weight is less than 400, the main component is bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA, relative molecular weight 340). To fix the amount of fixed bisphenol A and make excess epichlorohydrin can obtain DGEBA. The reaction process is as follows:
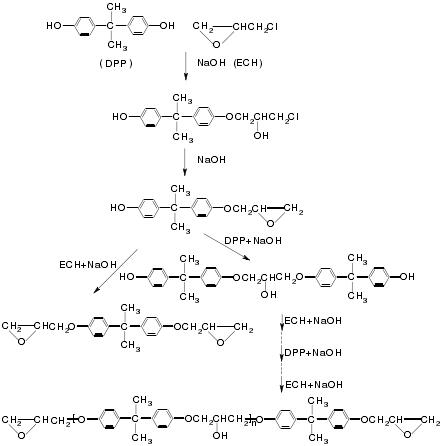
As can be seen from above, the product is bisphenol A diglycidyl ether when there is sufficient epichlorohydrin and enough sodium hydroxide as the catalyst. Excessive amounts of bisphenol A generate linear high molecular compounds with hydroxyl-, etherand epoxy-terminated groups. The internal rotation function of the ether bond increases the flexibility of the molecule, and the hydroxyl group enhances the chemical reactivity and the bonding ability, the epoxy group cross-links molecules into a three-dimensional network structure by reacting with a curing agent. The performance represented by each part of the Bisphenol A-type epoxy resin is shown here:
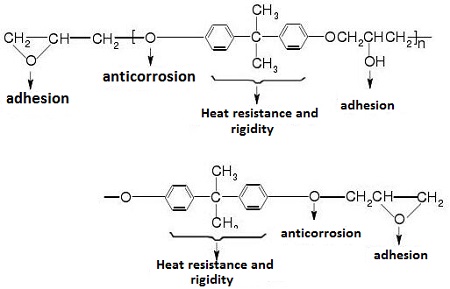
|
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
Araldite? 506 epoxy resin has been used as an embedding medium for microscopy. | [Uses]
PBE can be used as a reinforcing polymer on nanotubes and nanoparticles which can be useful in electronics, optical and aerospace based applications. It can also be used in the formation of solid polymeric electrolyte for potential application in electrochemical devices. | [General Description]
Poly(Bisphenol-A-co-epichlorohydrin) (PBE) is an epoxy based resin that is a phenoxy polymer derived from bisphenol A and epichlorohydrin. | [Solubility in organics]
Cellosolve acetate, MEK, THF | [Toxics Screening Level]
The ITSL for Bisphenol A/Epichlorohydrin resin is 160 μg/m3 based on an annual averaging time. |
|
|