| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
PENTAERYTHRITOL TRIALLYL ETHER | [CAS]
1471-17-6 | [Synonyms]
Triallyl pentaerythritol
PENTAERITHRITOLTRIALLYLETHER
Pentaerythrityl triallyl ether
PENTAERYTHRITOL TRIALLYL ETHER
Pentaerythritol Triallyl Ether,>75%
1-(2-naphthalenyl)-N-phenylethanimine
3-allyloxy-2,2-bis(allyloxymethyl)propan-1-ol
3-(allyloxy)-2,2-bis[(allyloxy)methyl]propanol
3-prop-2-enoxy-2,2-bis(prop-2-enoxymethyl)propan-1-ol
1-Propanol, 3-(2-propenyloxy)-2,2-bis[(2-propenyloxy)Methyl]-
1-Propanol, 3-(2-propen-1-yloxy)-2,2-bis[(2-propen-1-yloxy)methyl]- | [EINECS(EC#)]
216-008-4 | [Molecular Formula]
C14H24O4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00055654 | [MOL File]
1471-17-6.mol | [Molecular Weight]
256.34 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
Triallyl pentaerythritol (PEATA), a crosslinker, decreases the protein rejection compared to membranes functionalized with MBAA or without any crosslinker[1][2]. | [Application]
Crosslinkers and thickeners for superabsorbent polymers (SAP), unsaturated polyesters, UV curing resins, polyurethane resins, Carbomers.Also used in adhesives in powders coatings and emulsions. | [Synthesis]
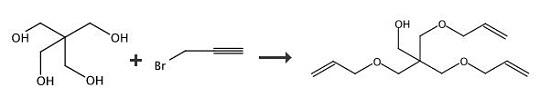
3-(Prop-2-ynyloxy)-2,2-bis((prop-2-ynyloxy)methyl)propan-1-ol (35). An aqueous solution of NaOH (40 wt %, 10 mL) was added to a solution of pentaerythritol (2.00 g, 14.7 mmol) in 15 mL of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The solution was stirred at rt for 30 min. Propargyl bromide (97%, 9.8 mL, 110 mmol) was then added, and the solution was kept at rt for an additional 10 h. The reaction mixture was then poured into 150 mL of EtOAc and washed with H2O (50 mL × 2) as well as brine (50 mL). The organic layer was dried by Na2SO4 and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated, and the residue was purified by FC (EtOAc/hexane = 1/4). 2.29 g of yellowish oil 35 (yield: 62%). 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 4.13 (d, 6H, J = 2.4 Hz), 3.69 (d, 2H, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.56 (s, 6H), 2.43 (t, 3H, J = 2.4 Hz). | [References]
[1] Polina Dobromirova Peeva, et al. Tuning the ultrafiltration properties of anti-fouling thin-layer hydrogel polyethersulfone composite membranes by suited crosslinker monomers and photo-grafting conditions. Journal of Membrane Science 362(2010)560-568.
[2] Polina Dobromirova Peeva, et al. Factors affecting the sieving behavior of anti-fouling thin-layer cross-linked hydrogel polyethersulfone composite ultrafiltration membranes. Journal of Membrane Science. Volumes 390–391, 15 February 2012, Pages 99-112. |
|
|